The complexity of modern cyber threats has caused a significant increase in companies’ average annual budget for cybersecurity. Measuring the efficiency of any investment and providing an argument about its future depends on the ROI metrics associated with it. However, the classic ROI concepts don’t seem appropriate for measuring security investment efficiency( (return of investment). That is why CISOs must know what ROI means in security to justify their budget usage.
What is the classic return on investment?
ROI metrics are optimized for measuring an average return on our investments (profitability). These metrics determine the value of investments individually, and in comparison with other investments. Using these metrics helps investors to measure their costs and profits. Let’s take a look at the basic formula for measuring ROI:
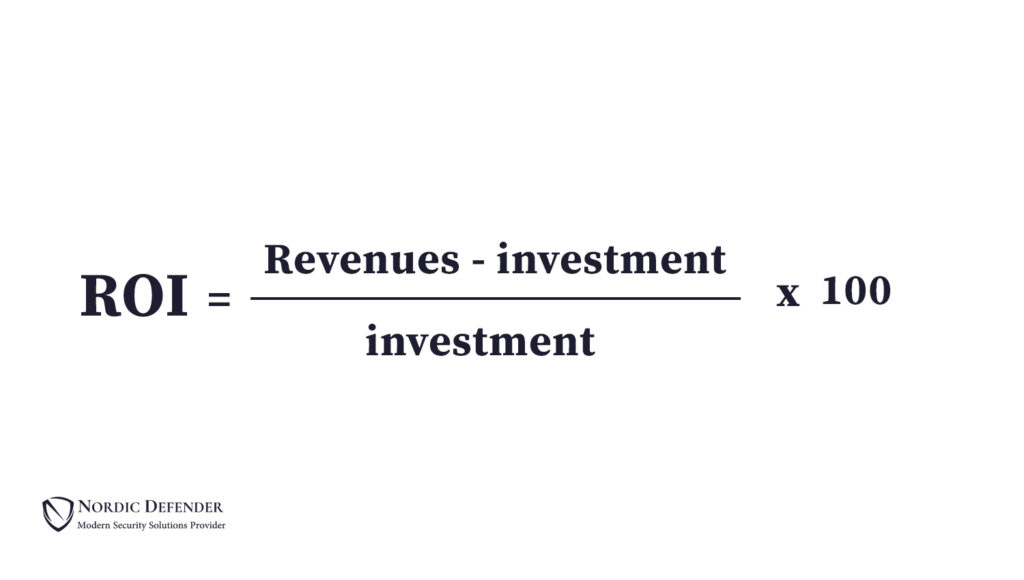
What does ROI mean in security?
RoI calculations are meant to indicate quantitative answers to essential questions that can be asked about any investments. Regardless of the industry in which we invest, there is always an optimized solution for applying the concept of ROI to our investing pathway. Such action will clarify the investment path for us, and let us know if we are paying too much, when we can say we have paid enough, and whether the investment is beneficial for us. Applying ROI metrics to security investment (Return of investment metric in security) can also answer the critical questions that justify our budget usage. With that all, there is no easy way to reach a clear insight into the revenues that security investments bring. Therefore the classic ROI formula can’t be used for measuring ROSI.
Why is it essential to measure ROSI?
Calculating ROSI determines whether our investment is profitable or not.
Determining the profitability of our investment is one of the numerous advantages that ROI calculation brings to our company. It also helps executive managers to estimate the company’s security states, and what is essential for achieving high-level security. In the other words, calculating ROSI gives you better insight into your security strategy and helps you enhance it. Therefore executive managers would be able to decide about adding new departments, hiring more experts, or buying new tools and services. Let’s take a look at how ROSI affects the various elements that shape a security strategy:
ROSI guides us toward the most perfect area for investing. Thus, executive managers would understand that investing in a specific department, solution, or area brings more profit to them, so they can examine the considered area for more investment opportunities.
On the other hand, calculating ROSI would also determine if the company is paying too much for paving a non-profit pathway. All in all, it is the ROSI calculation that shapes a company’s security strategy.
Rosi’s most common models
Comparing the monetary value of the security investments with the financial damages caused by possible attacks is the key to calculating ROSI. In the other words, the evaluation of the investments that have been made in order to security enhancement is based on the estimation of possible losses due to ignoring the importance of cyber security. The difference between ROSI calculation models arises from the difference between risk assessment methodologies.
Annual Rate of Occurrence
Annual Rate of Occurrence determines the probability of security breaches falling out. The elements that can affect this criterion directly or indirectly are so vast that should Be accurately estimated by cyber sec experts. The expert who is responsible for estimating Annual Rate of Occurrence should also be capable of predicting the effects of unexpected factors such as political geographic issues, disk failures due to the operating temperature, or physical data theft on ROA.
single Loss Expectancy
Single Loss Expectancy is the amount of money that is expected to be spent in case of a risk occurrence. It can also be calculated through estimating the total damages caused by an accident after one occurrence. SLE is the most complicated ROSI metric to be calculated, because each cyber occurrence consists of exclusive IT damages and a series of collateral damages. There are various solutions for calculating SLE. By choosing a specific solution to obtain this criterion, we must use the same solution in all our calculations.
Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE)
The ALE stands for Annual Loss Expectancy and this is how it is calculated: ALE= SLE*ARO
ROSI metrics are not meant for calculating financial benefits of investing in cybersecurity. In the other word, investing in cyber security doesn’t have any particular financial benefits, but it more about loss prevention. Therefore, it is better to avoid financial approaches when calculating ROSI.
The Limits of ROSI
Return on Security Investment (ROSI), refers to calculating the monetary value of the reduction in information security risks. By estimating the return on security investment value, we will have full insight into how our investment in data security is performing and what outcomes are available at the moment.
A thorough calculation of ROSI is a way of determining if a security control is worth implementation or not. In simple words, ROSI is calculated by evaluating the monetary risk for a specific incident and the cost of implementing a security control to mitigate that type of risk.
ROSI is a highly reliable method to understand some of the negative and positive impacts of security strategies, but there might be some limitations to this.
● The accuracy of statistical data used for ROSI calculation is essential, and this data may not be accurate in security incidents in organisations. To make the most of ROSI calculations, companies are in need of accurate data on how an incident can impact their systems to make use of the data in the ROSI formula without any concern.
● The time factor is not considered in the ROSI calculation. So if a company needs to know how investments return based on different durations, there is no idea.
● When using the return on security investment model, the calculation only includes financial gains. Auxiliary benefits, such as social benefits or brand growth, are not taken into account.
● Some costs may be omitted when using the ROSI method, such as insurance expenses or taxes. There is a need to include all expenses, such as maintenance costs, to get all the information about how cybersecurity strategies are performing in a company.
ROSI takes into account some essential factors, like annual loss expectancy (ALE), cost of the solution, and mitigation ratio, to evaluate the value of security investments spent in a specific period of time. All things considered and by neglecting some minor inaccuracies, the ROSI model is very useful to show how different cybersecurity solutions are working and comparing different values of ROSI will provide us with better decision-making.
Data Accuracy is Crucial
Data accuracy is a pivotal consideration when calculating the ROSI value in small to large organisations. Unfortunately, cyber threats and incidents impacting companies are constantly changing, and cybersecurity teams must be vigilant in collecting and using relevant data if they are tasked to calculate the return on security investment.
In some cases, there is little statistical data available about an incident or cyber threat since it could occur expeditiously. If there are no thorough monitoring tools and effective supervision over cyber threats and incidents, cybersecurity teams can not produce complete reports and incident statistics and they don’t have satisfactory insight into the real effectiveness of security strategies and implemented plans.

How to Overcome ROSI Limitations?
ROSI has some intrinsic limitations that may not be ignored, such as the inability to integrate some important factors into calculations. But, cybersecurity teams can improve calculations and solve most of the limitations by taking some essential steps.
1. Know What You Have and What You Need in the Future
The data security requirements and preferences in any company differ from company to company. It depends on the type of your company, the structure, the size, and the number of employees working in your organisation. The most effective ROSI may vary depending on the situation and the type of your company, and cybersecurity teams should take this into consideration. A good ROSI differs for different businesses since each of them has their own goals and plans.
2. How About Using Different Models of ROSI?
There is more than one ROSI model cybersecurity teams can use to calculate the return on security investments value. The classic calculation model of returns emphasises only the final results and investments. But, there are other useful models that are customised to provide better insight into a specific type of cyber incidents.
Unlike the simple ROSI model, specific formulas are based on the assessment of the specific risks related to a cyber incident.
3. Do You Agree with Choosing the Right Metrics for ROSI?
The return on investment of every cyber incident should be calculated based on the right metrics and reliable formulas. Cybersecurity teams have the knowledge and expertise to choose the best model, ensuring there will be the right information about a specific incident.
How to Arrange a Cyber Security Strategy Based on ROSI?
You would be surprised to know that achieving the best outcomes in ROSI depends on how a data security strategy has been defined, created, implemented, and controlled. A good cybersecurity strategy that includes all the requirements and future goals always results in the best ROSI.
A cybersecurity team will assess all the requirements at the first step and define the most effective strategy, ensuring the return on security investment is stable and high for implemented data security solutions.
To integrate security and protection into your organization and achieve good ROSI, consider the followings:
● Consult with a certified cybersecurity team
● Create effective cybersecurity policies
● Employ the latest data security technologies and best practices
● Develop a risk-based security strategy
● Bring attention to data loss prevention methodologies
● Implement a reliable access control strategy
● Always monitor and update your policies, data security plans, and strategies

